Recently, Professor Xu Yongqing, Director of Orthopaedics Department of the 920th Hospital of the Joint Service Support Force of the Chinese People’s Liberation Army, Professor Fan Xinyu, Deputy Director of Orthopaedics Department, and the medical team successfully applied the orthopedic surgical robot to the minimally invasive treatment of complex pelvic fractures, making a breakthrough in completing the first orthopedic surgical robot assisted pelvic fracture closed reduction and internal fixation operation in the whole process in southwest China.
The high-quality completion of the operation marks that the Department of Orthopaedics of the 920th Hospital of the Joint Service Support Force of the Chinese People’s Liberation Army has entered an era of intelligent, precise and minimally invasive treatment in the field of pelvic fractures. The hospital will accelerate the promotion of the concept and technology of minimally invasive diagnosis and treatment of orthopaedics to a new level, provide patients with more high-quality, convenient and low-risk diagnosis and treatment services, and lay a solid foundation for further innovation and opening up the development of digital and intelligent orthopaedics.
Ms. Zhang (pseudonym), who is in her 30s, suffered multiple pains throughout her body due to a car accident and was restricted from activities for 6 days (Tile B2.1 type). Before the operation, after full discussion by the medical and nursing teams such as Professor Xu Yongqing, the director of orthopaedics of the 920th Hospital of the Joint Support Force of the Chinese People’s Liberation Army, and Professor Fan Xinyu, the deputy director of orthopaedics, and considering that the patients are young women with serious injuries, and the traditional open reduction and internal fixation have a large amount of bleeding, it is recommended to use the world’s most advanced orthopaedic surgical robot to assist the whole process of closed reduction and internal fixation of pelvic fractures after full consideration.
Compared with traditional surgery, the use of intelligent orthopedic surgical robots can achieve minimally invasive treatment with “less trauma, fewer incisions, less bleeding, and less pain”, greatly reducing surgical risks, shortening patient recovery and hospitalization time, and reducing radiation exposure doses for patients and medical staff. Ms. Zhang agreed to accept the surgical plan and expressed her hope for a quick recovery and a return to normal life.
It is understood that pelvic fracture is a serious bone trauma, with high surgical treatment difficulty and risk, often accompanied by massive blood loss and other organ damage, and has always been recognized as a difficult point in the field of orthopedic trauma. Traditional open reduction surgery is highly invasive, time-consuming, and causes significant damage to patients. It is more likely to result in heavy bleeding, with intraoperative bleeding often reaching several thousand milliliters. Despite this, many patients are still unable to achieve satisfactory pelvic reduction, ultimately resulting in disability.
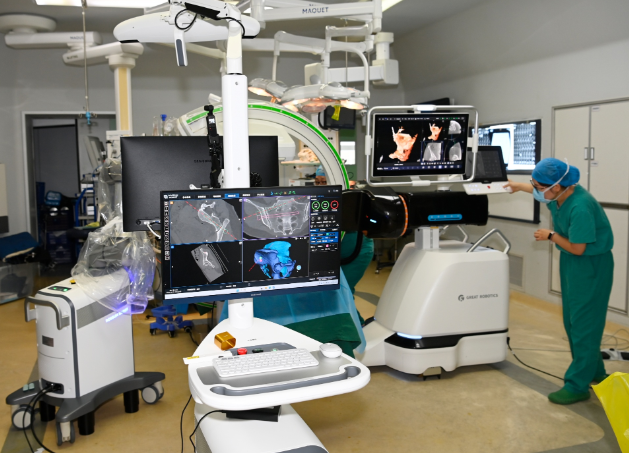
Before surgery, after careful preparation, based on the patient’s preoperative images, the medical team uses AI and big data based automatic surgical planning to mirror register the healthy limb of the patient. Through precise automatic segmentation and reconstruction, personalized and quantitative reduction planning is achieved. During the operation, the chief surgeons Xu Yongqing and Fan Xinyu achieved high-precision real-time dynamic 3D visualization navigation of the pelvis through preoperative and intraoperative image data fusion and registration. Under real-time dynamic 3D visualization navigation, robots were used to assist in precise and safe insertion of channel screws, and the surgery was successful. The patient had only 4 surgical incisions, with an average incision length of less than 1 centimeter and intraoperative bleeding of only 20 milliliters. After the surgery, Ms. Zhang recovered well and was able to walk on the ground within 3 weeks.
It is understood that with the advancement of technology and the continuous updating of surgical equipment, the application of intelligent devices such as robots to assist doctors in completing more accurate and minimally invasive surgeries has become an important development direction for orthopedic surgery.




