Powder metallurgy heats metals to a temperature just below their melting point to compact and mix the metal components. Since there is no true melting, the particles retain their unique properties. These metal powders can be elemental, partially alloyed, or pre-alloyed, allowing for the development of very unique and, more importantly, extremely precise metal compositions. Steel, iron, bronze, copper, and other metals are often used in powder metallurgy and other processes.
Powder metallurgy has three basic steps:
Stage 1
The primary component or material must first be ground into a powder. Several tools are available for this specific purpose. These mechanisms use pulverization, chemical reduction, electrolytic methods, mechanical alloying, atomization, and flaking, with the latter two being the most popular, to turn the raw metal into a powder or finely divided metal.
Stage 2
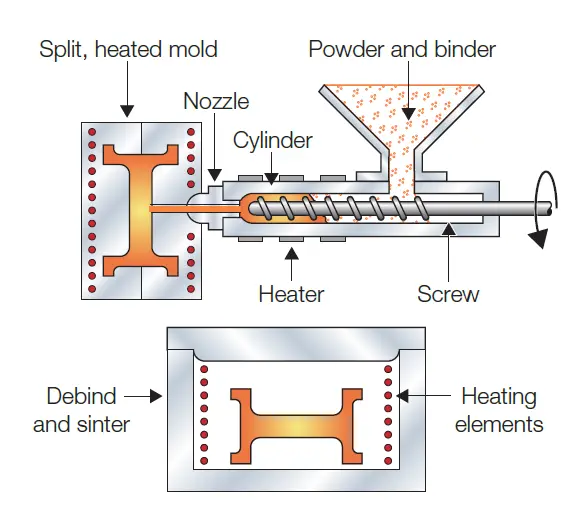
Afterwards, the particles are pumped into compact dies. These dies provide structural constraints for the structure of the final product. Powder metallurgy excels in producing complex parts that require bends, ridges, and depressions when the mold is made.
Stage 3
Compacting is the last step after the mold is filled. As with the first stage, different compaction procedures can be employed. Cold isostatic pressing, uniaxial pressing, sintering, hot isostatic pressing, hot powder forging, and metal injection molding are all possible. Each method requires significant pressure, but cold pressing procedures must use greater pressure to achieve the bonding that can be achieved with hot compaction. The result is a solid metal with different properties and porosity. In addition to the mechanism employed, various factors must be considered, including metal selection, finished product size, and number of pieces produced.
Applications of Powder Metallurgy:
– Used to make porous components such as filters
– Powder metallurgy makes some of the tungsten parts used in jet engines.
– Automotive moving parts such as piston rings, connecting rods, clutch plates, and camshafts
– Various soft and hard magnetic components
– Steel and diamond powders are used to make grinding wheels.
– Silver-impregnated tungsten is used to make nozzles for rockets and missiles.
– It is used to make parts with complex shapes, such as gears, that would require machining when made using other techniques.
– Metallic and non-metallic materials are combined to make electrical bushings for electric motors.
– Powder metallurgy can be used to make parts for clocks, typewriters, calculators, permanent magnets, and more.
Advantages of Powder Metallurgy
Environmentally friendly
Powder metallurgy is an environmentally friendly production technology. With powder metallurgy, 97% of the material needed to make a part ends up in the finished product. Powder metallurgy produces virtually no waste and no scrap. The final component contains all the powder particles used in the process. Not only is there less waste, but a lot of money can be saved as a result.
Flexibility in materials used and products produced
Compared to other processes, powder metallurgy can combine and mix a wide range of metals and non-metals into one product. With the help of binding materials, odd and unusual combinations can be combined into one component. Since powder metallurgy can mix and crush a variety of elements into a single shape, complex metallurgical techniques can be avoided. Powder metallurgy can create any shape, from simple gears to complex designs. The continuous development of the technology has opened the door to a wide range of applications.
Almost Net Shape
Parts and products made with powder metallurgy do not require any additional processing. Each component is almost a net shape, so there is no need for finishing. Powder metallurgy parts also have extremely high dimensional accuracy.

Available and economical raw materials
The availability of raw materials has been a long-standing problem for manufacturing processes, as shortages can slow or stop production. Powder metallurgy can use readily available and affordable raw materials. Metal powder is a relatively common, everyday material that is easily available from a wide range of producers. As the demand for powder metallurgy increases, more and more suppliers are creating manufacturing processes to meet this demand.
Repeatability of product accuracy
Every part produced in large quantities must meet the dimensional specifications specified in the design from beginning to end. However, degradation at certain steps in the production process can cause defects and differences in individual parts. The consistency and repeatability of the powder metallurgy process prevents such errors, ensuring that each part is dimensionally accurate.
Limitations of powder metallurgy
Powdered materials are quite expensive.
The manufacturing of complex products is challenging because metal powders do not flow well during the pressing process.
The remaining porosity in the sintered part makes its surface rough.
The process is only suitable for large-scale production due to the high cost of molds and equipment.
The cost of producing large size and weight parts is very high due to the expensive molds.
Some metal powders are difficult to compress, and some are difficult to find.
The density of the compact is not constant.
Parts produced by powder metallurgy have lower impact and fatigue strengths than other methods.
Powder metallurgy may contribute to health issues from air pollution in the workplace.
Shenzhen Yujiaxin Technology Co., Ltd., as a leader in the field of metal powder metallurgy processing, has always been dedicated to the development of this high-tech industry. With profound industry experience and advanced technical strength, the company is committed to providing full-chain processing services for metal powder preparation, forming, sintering, and more. In the popular field of metal powder metallurgy, Yujiaxin Technology not only masters key technologies such as powder mixing, pressing, and sintering, but also continuously innovates and develops a series of high-performance, high-precision metal powder metallurgy products. These products are widely used in high-tech industries such as automotive, aerospace, electronics, and medical devices, meeting the urgent market demand for high-quality metal components. Focusing on metal powder metallurgy, Yujiaxin Technology continuously drives industrial upgrading and provides customers with one-stop, customized solutions, helping them stand out in the fiercely competitive market.




